أنت تستخدم أحد المتصفحات القديمة. قد لا يتم عرض هذا الموقع أو المواقع الأخرى بشكل صحيح.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية للمبتدئين
تنقسم الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية إلى ثلاثة أزمنة (ماضي - مضارع - مستقبل) ، ولهذه الأزمنة الثلاثة أكثر من حال ، و ما يهمنا من هذه الأحوال إلا الأكثر شيوعا و استخداما في المحادثات العادية ، و هي (بسيط - مستمر - تام) ؛ فهذا الشرح سيكون بمثابة حجر أساس لبنائك اللغوي ، و بما أننا تحدثنا في مجال البناء ؛ فدعونا نمثل ببناية من ثلاثة أدوار ، و في كل دور ثلاث شقق ، و كل شقة تمثل زمنا ؛ فالشقة الأولى في كل دور تمثل الماضي ، و الشقة الثانية تمثل المضارع ، و الشقة الثالثة تمثل المستقبل . و كل دور يمثل حالة الزمن ؛ فالدور الأول يمثل الحال البسيط ، و الدور الثاني يمثل المستمر ، و الدور الثالث يمثل التام ، و بعد معرفة هذه الأدوار تستطيع الصعود إلى أدوار أخرى لاحقا .
بعد أن انتهينا من هذه البناية ؛ ينبغي أن يكون هناك متسع لأدوار إضافية تبنيها لاحقا بعد الانتهاء من معرفة هذه الأدوار ؛ فهناك - كما أسلفنا - التام المستمر و إخوانه . و أيضا يجب أن يكون بجوار هذه البناية مستودع منظم و مقسم ؛ فقسم (أ) للضمائر المنفصلة (أنا - أنت - هو ، هم .. إلخ) ، و قسم (ب) لتصريف الأفعال ، و قسم (ج) للأفعال المساعدة ، و قسم (د) و هو أكبر الأقسام للكلمات الإنجليزية المهمة ، و قسم (هـ) للمواضيع المتفرقة ، و عليك لاحقا أن تضيف أقساما جديدة ؛ بما تظنه يحتاج لقسم جديد . انظر إلى المستودع الذي أنشأناه الآن:
تجد بعض الأمثلة للأفعال العادية ، و بعض الأمثلة للأفعال الشاذة .
الأفعال العادية هي الأكثر و تضيف ed في آخر الكلمة للتصريفين الثاني (الماضي البسيط) و الثالث .
أما الأفعال الشاذة فلكل فعل منها تصريفه الخاص للماضي البسيط ، وللتصريف الثالث ، و عليك حفظها كاملة ؛ فهي تسمى الأفعال الشاذة لأنها تشذ عن القاعدة ، و تسمى أحيانا الأفعال الشائعة ؛ لأنها تستخدم بكثرة في المحادثات اليومية ؛ فعليك حفظها و الاهتمام بها .
القسم الثالث من مستودعنا هو قسم ج و هو قسم الأفعال المساعدة . و الأفعال المساعدة تبقى أفعالا لها تصريفات ثلاث كما مر عليك ؛ فلها مضارع ، و ماضي بسيط ، و تصريف ثالث .
الأفعال المساعدة هي:
am, is, are
و هذه صيغ التصريف الأول منها ، و هو المضارع .
أما صيغ الماضي ؛ فهي :
was, were
انظر إلى الجدول :
infinitive تعني الفعل في حالته الأصلية أو سمه المضارع .
past simple تعني صيغة الماضي البسيط للفعل .
past participle تعني التصريف الثالث للفعل .
لا حظ أن be تتفرع إلى (am - is - are) ؛ فنستخدم be في مواضع ، و نستخدم (am - is - are) في مواضع ، و سيتبين لك ذلك لاحقا ؛ فلا تتوقف كثيرا هنا .
قبل أن نبدأ في الدخول إلى الأدوار و الأزمنة ؛ علينا أن نتعرف على تركيب الجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ فالجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية لا بد لها من ثلاثة أشياء لتصبح صحيحة و شرعية:
أولا : فاعل و هو من يقوم بالعمل في الجملة مثلا : أحمد يذهب إلى المدرسة ؛ أين الفاعل هنا ؟ أو من يذهب إلى المدرسة ؟ الجواب: أحمد ؛ إذن أحمد هو الفاعل .
وكذا لو قلنا يزرع الرجال الحقل .
من يزرع الحقل ؟ الجواب الرجال إذن الرجال هم الفاعل .
إذن الفاعل هو من يقوم بالفعل أو لتسهيلها خذ الفعل في الجملة ، و اسأل نفسك من الذي يقوم بهذا الفعل ؟ و هذا سيدلك على الفاعل .
خالد يشرب الماء ... من الذي يشرب الماء ؟
هند تدرس البنات .. من التي تـُدرس ؟
أعلم أن عقلك يلح عليك بالتفكير في الجملة في اللغة العربية و مقارنتها ، و سأتغاضى عن ذلك و أشرح ذلك الفرق بينهما .
هناك نوعان للجملة في اللغة العربية ، و هما جملة اسمية ، و جملة فعلية .
و الجملة الاسمية هي ما تبتدأ باسم .
أحمد يشرب الماء .
أحمد هو اسم و هو أول كلمة في الجملة ؛ إذن الجملة اسمية .
و لكن إذا قلنا :
يشرب أحمد الماء ..
بماذا ابتدأت الجملة ؟
ابتدأت بـ يشرب و هي فعل ؛ إذن الجملة فعلية .
هذه ببساطة الجملة الاسمية و الفعلية في اللغة العربية.
في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ لا يوجد هذا الشيء ؛ فكل الجمل عندهم اسمية ، و لا تستطيع ابتداء الكلام بالفعل ؛ بل لا بد أن تبدأ بالاسم .
جملة : أحمد يلعب كرة القدم ؛ أين الاسم أو بالأصح أين الفاعل الذي يلعب كرة القدم ؟ الجواب أحمد إذن نأخذ أحمد ، و نبتدأ به الكلام في الجملة الإنجليزية .
الخطوة الأولى: إضافة الفاعل ، و هو أحمد ؛ فتكون جملتنا:
Ahmed ..
فهذا أول ما يوضع في الجملة الإنجليزية ، و هو الفاعل ، و تستطيع استخدام ضمير ينوب عنه فـ "هو" تنوب عن أحمد و "هم" تنوب عن الرجال .
إذن أول ما تحتاجه الجملة الإنجليزية هو الفاعل أو subject
ثانيا: الفعل verb ، و هو ما يقوم به الفاعل ؛ فإذا أخذنا جملتنا السابقة : أحمد يلعب كرة القدم ، وسألنا أنفسنا من يلعب كرة القدم ؛ فسيكون الجواب: أحمد إذن أحمد هو الفاعل . نسأل أنفسنا مرة أخرى : ماذا يفعل أحمد ؟ الجواب: يلعب. إذن يلعب هي الفعل ؛ فنضيفه إلى أحمد لتصبح الجملة:
Ahmed plays ..
و الفعل هذا من أساسيات الجملة الإنجليزية ، و لا تتم إلا به و بالفاعل .
(لاحظ أننا أضفنا s إلى الفعل ، و ذلك بسبب زمن الفعل ، و سنشرح ذلك في المضارع المستمر)
ثالثا: المفعول به object : و على الرغم من أنه الجزء الثالث من أركان الجملة الإنجليزية إلا أنهم أحيانا يتجاهلونه ، و يكتفون بالفاعل و الفعل فقط ، و في تلك الحالة يجب أن يكون الفعل من الأفعال اللازمة أو القوية التي لا تحتاج لمفعول به ليشرحها ؛ مثلا : أحمد مات . انتهى الموضوع ، و لا يوجد شرح إضافي لهذا .
Ahmed died
تمت الجملة الإنجليزية هنا ، و تجاهلت المفعول به ؛ لأن الفعل كان قويا جدا .
و على الرغم من الأفعال القوية تتجاهل المفعول به إلا أنه يبقى للأفعال الأخرى الضعيفة التي لا تستطيع إيصال المعنى كاملا بدون مفعول به كأحمد يشرب الماء ؛ فلو قلنا أحمد يشرب ؛ لتسائلنا عما يشربه فهناك الكثير من الاحتمالات ؛ فهل يشرب عصيرا أم ماء أم خمرا و العياذ بالله !
إذن المفعول به يبقى الجزء الأخير من الجملة ، و لإعطائه مكانا معنويا أكثر ؛ فهو يشمل باقي الجملة التي تلي الفعل ؛ فبعد أن تقول أحمد يتناول .. يأتي المفعول به و يضم كل شيء ستقوله بعد يتناول ؛ فقد تقول: البوظة في الحديقة ؛ فتصبح : البوظة في الحديقة مفعولا به ، و هذا لا ينطبق في اللغة العربية بل هو خاص للغة الإنجليزية.
إذن أركان الجملة الإنجليزية ثلاثة:
فاعل Subject – فعل Verb – مفعول به object
و يجب أن تسير على هذه القاعدة دائما ؛ فلا تستطيع البداية بالفعل ، و إلا أصبحت جملتك غير شرعية .
احفظ هذه القاعدة ، و عود نفسك عليها عندما تقرأ أي كلام إنجليزي ؛ فاستخرج الفاعل و الفعل و المفعول به دائما حتى ترسخ في ذهنك ، و عندما تحاول إنشاء جملة إنجليزية من عندك فاعملها على هذا الترتيب الذي تعلمناه : فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به .
و بالطبع هناك بعض الكماليات للجملة ، و لكنها لا تهمك في الوقت الحاضر.
الآن خذ هذه الجمل الإنجليزية ، و استخر الفاعل ، و الفعل ، و المفعول به .
تدريب 1:
Scrooge never painted out Old Marley’s name. There it stood, years afterwards, above the warehouse door: Scrooge and Marley. The firm was known as Scrooge and Marley. Sometimes people new to the business called Scrooge Scrooge, and sometimes Marley, but he answered to both names. It was all the same to him.
و الآن دعنا نعود للدور الأول من البناية التي بنيناها ، و نبدأ معا ؛ نلاحظ أن البسيط أخذ الثلاثة أزمنة ؛ فهناك ماضي بسيط ، و مضارع بسيط ، و مستقبل بسيط ، و البسيط هو - كما يتضح من اسمه - أبسط التراكيب ، و أبعدها عن التعقيد ؛ فهو لا يعتمد على أية أفعال مساعدة.
لنبدأ بالماضي البسيط past simple :
أنا عملت في بنك من عام 1999 إلى عام 2004
هذه الجملة تتكون من : الضمير المنفصل (أنا)
و الفعل بصيغة الماضي (عمل)
و بقية الجملة (في بنك من عام ... إلخ) .
لنحولها إلى اللغة الإنجليزية ، و نستخرج من المستودع الذي رسمناه سابقا ما نريد :
لنذهب أولا إلى قسم (أ) حيث الضمائر المنفصلة ؛ فنجد أن أنا تعني I .
نتوجه ثانيا إلى قسم (ب) حيث تصريف الأفعال (العادية و الشاذة) ، و عمل تعني work و هي من الأفعال العادية أو القياسية ؛ فيكون الماضي البسيط منها أو التصريف الثاني ، و هو ما نستخدمه في زمن الماضي هو: worked
بقية الجملة (في بنك من عام ... إلخ) = in a bank from 1999 to 2004
فلنضع ما بحوزتنا معا :
I worked in a bank from 1999 to 2004
و هذا هو الماضي البسيط ، و تستطيع إضافة زمن لتحديده كما فعلنا ؛ فالماضي البسيط ليس محدد بزمن معين بل يعني فترة سابقة غير محددة ؛ فإذا قلت أنا عملت في بنك I worked in a bank ؛ فهذا له أكثر من احتمال ؛ فقد تكون تقصد البارحة أو قبل خمس سنوات ، و لن يستطيع أحد معرفة الوقت الذي عملت فيه في البنك إلا إذا حددت ذلك .
الخلاصة :
الماضي البسيط يعتمد – ككل الأزمنة القادمة – على تركيب الجملة الإنجليزية ؛ فالجملة الإنجليزية تتكون – كما عرفنا – من فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به . و عندما نريد جعل الجملة في حال الماضي البسيط ؛ فإننا نقوم بتحويل الفعل فقط إلى تصريف الماضي البسيط ، و تبقى الجملة كما هي عليه ، و سيتبين لك الفرق أكثر بعد دراستك لبقية الأزمنة ، و المقارنة بينها ؛ فلا تستعجل .
انتهينا من الشقة الأولى في الدور الأول من بنايتنا ، و هي الماضي البسيط ، و نتوجه الآن إلى جارتها الشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع البسيط.
المضارع البسيط يعني الاستمرار في عمل الشيء ، و ليس استمرار مؤقتا ؛ بل استمرار دائما يوميا أو أسبوعيا أو شهريا . مثال ذلك : أنا أذهب إلى المدرسة كل يوم . I go to school (every day)
فهذا يفيد الاستمرار اليومي للذهاب إلى المدرسة .
وإذا أردنا قاعدته الإنجليزية ؛ فهي أن نأخذ التصريف الأول للفعل الذي سميناه المضارع .
دعونا نأخذ جملة جديدة ، و نشرحها بدلا من جملتنا السابقة ، خذ مثلا :
أحمد يعمل في مكتبة .
لدينا هنا : أحمد – يعمل
أحمد ترجمتها : Ahmed ؛ فهي اسم .
يعمل work
انتبه هنا لشيء يميز المضارع البسيط ، و هو أن الفعل للمفرد يأخذ s بينما الجمع ؛ فيبقى الفعل بصيغته ، و نعني بالمفرد يعمل أو تعمل أما الجمع ؛ فهو يعملون تعملن تعملان .. إلخ .
ولتسهيلها عليك فالفعل الذي يأتي بعد:
He, She, It
يكون مفردا
أما الفعل الذي يأتي بعد:
I, You, They, We
فيكون جمعا .
لعلك تتساءل الآن لماذا أدخلنا I و التي بمعنى "أنا" و You و التي بمعنى "أنت" إلى قائمة الجمع .
حسنا (أنا) و (أنت) تستخدم بصيغة الجمع للمخاطب ؛ فهم يستخدمونها للتفخيم ؛ مثلا عندما تريد أن تفخم المخاطب ، و تقول له: حضرتكم يا سيادة الرئيس كذا و كذا .. فأنت استخدمت الجمع على الرغم من أن الرئيس مفرد ، و لكنك استخدمتها للتفخيم ، و كذا الحال عند الحديث عن نفسك بصيغة الجمع : قرأنا خطابكم الكريم . فأنت تستخدم صيغة الجمع ، و الفرق بين العربية و الإنجليزية أن الإنجليزية تستخدمها دائما بصيغة الجمع أما في العربية ففي بعض الحالات ، و على الرغم من هذا التعليل إلا أنك يجب أن تعرف أن اللغة الإنجليزية لا يشترط أن يكون لها تعليل ؛ بل أحيانا تضطر لأخذ ما فيها بدون تعليل ؛ بل هكذا هم يتحدثون ، و هذه هي قواعدهم ؛ فانتبه أن تبحث دوما عن التفسير أو المقارنة باللغة العربية ؛ فسيدخلك ذلك في حيرة .
نعود لحديثنا عن المضارع البسيط ؛ فهو يعطي :
I, You, They, We
صيغة الفعل الأصلية في التصريف ، مثال:
I go to school every day
We work in a bank
فلاحظ الفعلين : go, work بقيا على حالتها الأصلية وهو التصريف الأول للفعل بدون أي إضافات.
أما في :
He, She, It
فتضيف s على الفعل ، و مثال ذلك :
He goes to school every day
It drinks milk
لاحظ أننا أضفنا إلى الفعلين: go, drink حرف s و ذلك من أجل أنها أتت بعد :
He, she, it
سواء حددت أن ذلك يتم كل يوم أو أسبوع أم لم تحدد ذلك ؛ فعندما تستخدم المضارع البسيط ؛ فسيفهم من كلامك الاستمرارية يوميا أو أسبوعيا .. إلخ ، و أن هذا يحدث بشكل دوري ، و لك الحرية بتحديد ذلك أو جعله مبهما إذا لم يكن مهما ؛ فمثلا عندما تريد أن تخبر أحدا أنك تلعب كرة القدم باستمرار ؛ فستقول :
I play football (soccer)
و سيعلم المستمع أن تلعب كرة القدم باستمرار ، و هذا ما أعطاك لياقة بدنية عالية مثلا ؛ فلا يحتاج أن يعلم الوقت هل هو يومي أم غير ذلك ، و الأمر كله يعود إليك في تحديد ذلك .
في الجملة الأخيرة استخدمنا كلمة Football و Soccer وكلاهما يعني كرة القدم ، و لكن Football مستخدمة في الأمم المتحدة (بريطانيا و أخواتها) أما Soccer فتستخدم في أمريكا ، و لو استخدمت Football في أمريكا فسيظنونك تقصد كرة القدم الأمريكية ، و التي فيها الركل و استخدام الكرة باليد .. إلخ !
و هكذا انهينا من المضارع البسيط ؛ فهو يفيد الاستمرار اليومي الأسبوعي أو حتى كل ساعة ، و لكنه بشكل عام يفيد الاستمرار بأنك تعمل ذلك من وقت لآخر بترتيب معين .
و نضيف S للأفعال المفردة ، و يبقى الفعل بحالته الأصلية لأفعال الجمع .
الخلاصة:
المضارع البسيط يفيد حدوث الشيء بشكل دوري ، يومي .. أسبوعي .. سنوي .. إلخ .
و قاعدته أنك تغير الفعل في الجملة الإنجليزية التي تعلمنا سابقا أركانها الثلاث ؛ فتأخذ الفعل بصيغة المضارع ، و هي التصريف الأول للفعل ، و تضيف إليه حرف s إذا أتى بعد He, she, it ، و لا تضيف له شيئا إذا أتى بعد: I, You, They, We
نذهب الآن للشقة الأخيرة في الدور الأول ، و هي المستقبل البسيط ,
قاعدة المستقبل البسيط كسولة جدا ؛ فهي لا تملك سوى Will و تضيفها لقاعدة المضارع البسيط ، و لكنها لا تعتبر بالجمع أو المفرد فلا تضيف s ؛ بل يبقى الفعل في حالته الأصلية . مثال:
أنا سأذهب إلى المدرسة غدا .
I will go to school tomorrow
هو سيذهب إلى المدرسة غدا
He will go to school tomorrow
لاحظ أننا لم ننظر للفعل هل هو مفرد أم جمع بل أخذناه بصيغته الأصلية في التصريف ، و أضفنا قبله كلمة Will و التي تعني سوف ، و انتهينا .
أما ما يفيد به المستقبل البسيط ؛ فهو الحديث عن المستقبل بشكل مبهم أيضا ، و تستطيع تحديد ذلك أو تجاهله كما سبق الحديث عن ذلك في المضارع البسيط ؛ فتستطيع القول: أنا سأسافر غدا أو أنا سأسافر . و اختيارك للألفاظ يعتمد على حاجة المتلقي .
أمثلة:
أنا سأجتهد في الامتحان .
I will work hard in the exam
هو سيجتهد في الامتحان
He will work hard in the exam
الخلاصة: المستقبل البسيط يأخذ الفعل بحالته الأصلية أو التصريف الأول (المضارع) له ، و يضيف قبل ذلك Will فقط بغض النظر عن نوع الفاعل قبله ؛ فكل الضمائر : I, You, They, We, He, she, it يأتي بعدها will ثم الفعل بتصريفه الأول دون أن نضيف s على أي منها . ويفيد المستقبل البسيط بالإخبار عن حدث سيكون في المستقبل ، و لكن بشكل مبهم و دون معرفة وقته المحدد ، و يعود إليك تحديد الوقت .
انتهينا من الأزمنة البسيطة ، و هي الماضي البسيط ، و المضارع البسيط ، و المستقبل البسيط .
تدريب 2:
حدد نوع الجملة ، و من أي الأزمنة هي ، ثم حولها إلى الزمنين البسيطين الآخرين:
We had the carriage
He cleaned his teeth
It will rain tomorrow
They play tennis
You will watch television
She speaks Spanish
مثال للحل:
We had the carriage
زمن الجملة: ماضي بسيط
تحويلها إلى:
المضارع البسيط:
We have the carriage
المستقبل البسيط:
We will have the carriage
انتهى الدور الأول كاملا .
منقووول
تنقسم الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية إلى ثلاثة أزمنة (ماضي - مضارع - مستقبل) ، ولهذه الأزمنة الثلاثة أكثر من حال ، و ما يهمنا من هذه الأحوال إلا الأكثر شيوعا و استخداما في المحادثات العادية ، و هي (بسيط - مستمر - تام) ؛ فهذا الشرح سيكون بمثابة حجر أساس لبنائك اللغوي ، و بما أننا تحدثنا في مجال البناء ؛ فدعونا نمثل ببناية من ثلاثة أدوار ، و في كل دور ثلاث شقق ، و كل شقة تمثل زمنا ؛ فالشقة الأولى في كل دور تمثل الماضي ، و الشقة الثانية تمثل المضارع ، و الشقة الثالثة تمثل المستقبل . و كل دور يمثل حالة الزمن ؛ فالدور الأول يمثل الحال البسيط ، و الدور الثاني يمثل المستمر ، و الدور الثالث يمثل التام ، و بعد معرفة هذه الأدوار تستطيع الصعود إلى أدوار أخرى لاحقا .
بعد أن انتهينا من هذه البناية ؛ ينبغي أن يكون هناك متسع لأدوار إضافية تبنيها لاحقا بعد الانتهاء من معرفة هذه الأدوار ؛ فهناك - كما أسلفنا - التام المستمر و إخوانه . و أيضا يجب أن يكون بجوار هذه البناية مستودع منظم و مقسم ؛ فقسم (أ) للضمائر المنفصلة (أنا - أنت - هو ، هم .. إلخ) ، و قسم (ب) لتصريف الأفعال ، و قسم (ج) للأفعال المساعدة ، و قسم (د) و هو أكبر الأقسام للكلمات الإنجليزية المهمة ، و قسم (هـ) للمواضيع المتفرقة ، و عليك لاحقا أن تضيف أقساما جديدة ؛ بما تظنه يحتاج لقسم جديد . انظر إلى المستودع الذي أنشأناه الآن:
تجد بعض الأمثلة للأفعال العادية ، و بعض الأمثلة للأفعال الشاذة .
الأفعال العادية هي الأكثر و تضيف ed في آخر الكلمة للتصريفين الثاني (الماضي البسيط) و الثالث .
أما الأفعال الشاذة فلكل فعل منها تصريفه الخاص للماضي البسيط ، وللتصريف الثالث ، و عليك حفظها كاملة ؛ فهي تسمى الأفعال الشاذة لأنها تشذ عن القاعدة ، و تسمى أحيانا الأفعال الشائعة ؛ لأنها تستخدم بكثرة في المحادثات اليومية ؛ فعليك حفظها و الاهتمام بها .
القسم الثالث من مستودعنا هو قسم ج و هو قسم الأفعال المساعدة . و الأفعال المساعدة تبقى أفعالا لها تصريفات ثلاث كما مر عليك ؛ فلها مضارع ، و ماضي بسيط ، و تصريف ثالث .
الأفعال المساعدة هي:
am, is, are
و هذه صيغ التصريف الأول منها ، و هو المضارع .
أما صيغ الماضي ؛ فهي :
was, were
انظر إلى الجدول :
infinitive تعني الفعل في حالته الأصلية أو سمه المضارع .
past simple تعني صيغة الماضي البسيط للفعل .
past participle تعني التصريف الثالث للفعل .
لا حظ أن be تتفرع إلى (am - is - are) ؛ فنستخدم be في مواضع ، و نستخدم (am - is - are) في مواضع ، و سيتبين لك ذلك لاحقا ؛ فلا تتوقف كثيرا هنا .
قبل أن نبدأ في الدخول إلى الأدوار و الأزمنة ؛ علينا أن نتعرف على تركيب الجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ فالجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية لا بد لها من ثلاثة أشياء لتصبح صحيحة و شرعية:
أولا : فاعل و هو من يقوم بالعمل في الجملة مثلا : أحمد يذهب إلى المدرسة ؛ أين الفاعل هنا ؟ أو من يذهب إلى المدرسة ؟ الجواب: أحمد ؛ إذن أحمد هو الفاعل .
وكذا لو قلنا يزرع الرجال الحقل .
من يزرع الحقل ؟ الجواب الرجال إذن الرجال هم الفاعل .
إذن الفاعل هو من يقوم بالفعل أو لتسهيلها خذ الفعل في الجملة ، و اسأل نفسك من الذي يقوم بهذا الفعل ؟ و هذا سيدلك على الفاعل .
خالد يشرب الماء ... من الذي يشرب الماء ؟
هند تدرس البنات .. من التي تـُدرس ؟
أعلم أن عقلك يلح عليك بالتفكير في الجملة في اللغة العربية و مقارنتها ، و سأتغاضى عن ذلك و أشرح ذلك الفرق بينهما .
هناك نوعان للجملة في اللغة العربية ، و هما جملة اسمية ، و جملة فعلية .
و الجملة الاسمية هي ما تبتدأ باسم .
أحمد يشرب الماء .
أحمد هو اسم و هو أول كلمة في الجملة ؛ إذن الجملة اسمية .
و لكن إذا قلنا :
يشرب أحمد الماء ..
بماذا ابتدأت الجملة ؟
ابتدأت بـ يشرب و هي فعل ؛ إذن الجملة فعلية .
هذه ببساطة الجملة الاسمية و الفعلية في اللغة العربية.
في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ لا يوجد هذا الشيء ؛ فكل الجمل عندهم اسمية ، و لا تستطيع ابتداء الكلام بالفعل ؛ بل لا بد أن تبدأ بالاسم .
جملة : أحمد يلعب كرة القدم ؛ أين الاسم أو بالأصح أين الفاعل الذي يلعب كرة القدم ؟ الجواب أحمد إذن نأخذ أحمد ، و نبتدأ به الكلام في الجملة الإنجليزية .
الخطوة الأولى: إضافة الفاعل ، و هو أحمد ؛ فتكون جملتنا:
Ahmed ..
فهذا أول ما يوضع في الجملة الإنجليزية ، و هو الفاعل ، و تستطيع استخدام ضمير ينوب عنه فـ "هو" تنوب عن أحمد و "هم" تنوب عن الرجال .
إذن أول ما تحتاجه الجملة الإنجليزية هو الفاعل أو subject
ثانيا: الفعل verb ، و هو ما يقوم به الفاعل ؛ فإذا أخذنا جملتنا السابقة : أحمد يلعب كرة القدم ، وسألنا أنفسنا من يلعب كرة القدم ؛ فسيكون الجواب: أحمد إذن أحمد هو الفاعل . نسأل أنفسنا مرة أخرى : ماذا يفعل أحمد ؟ الجواب: يلعب. إذن يلعب هي الفعل ؛ فنضيفه إلى أحمد لتصبح الجملة:
Ahmed plays ..
و الفعل هذا من أساسيات الجملة الإنجليزية ، و لا تتم إلا به و بالفاعل .
(لاحظ أننا أضفنا s إلى الفعل ، و ذلك بسبب زمن الفعل ، و سنشرح ذلك في المضارع المستمر)
ثالثا: المفعول به object : و على الرغم من أنه الجزء الثالث من أركان الجملة الإنجليزية إلا أنهم أحيانا يتجاهلونه ، و يكتفون بالفاعل و الفعل فقط ، و في تلك الحالة يجب أن يكون الفعل من الأفعال اللازمة أو القوية التي لا تحتاج لمفعول به ليشرحها ؛ مثلا : أحمد مات . انتهى الموضوع ، و لا يوجد شرح إضافي لهذا .
Ahmed died
تمت الجملة الإنجليزية هنا ، و تجاهلت المفعول به ؛ لأن الفعل كان قويا جدا .
و على الرغم من الأفعال القوية تتجاهل المفعول به إلا أنه يبقى للأفعال الأخرى الضعيفة التي لا تستطيع إيصال المعنى كاملا بدون مفعول به كأحمد يشرب الماء ؛ فلو قلنا أحمد يشرب ؛ لتسائلنا عما يشربه فهناك الكثير من الاحتمالات ؛ فهل يشرب عصيرا أم ماء أم خمرا و العياذ بالله !
إذن المفعول به يبقى الجزء الأخير من الجملة ، و لإعطائه مكانا معنويا أكثر ؛ فهو يشمل باقي الجملة التي تلي الفعل ؛ فبعد أن تقول أحمد يتناول .. يأتي المفعول به و يضم كل شيء ستقوله بعد يتناول ؛ فقد تقول: البوظة في الحديقة ؛ فتصبح : البوظة في الحديقة مفعولا به ، و هذا لا ينطبق في اللغة العربية بل هو خاص للغة الإنجليزية.
إذن أركان الجملة الإنجليزية ثلاثة:
فاعل Subject – فعل Verb – مفعول به object
و يجب أن تسير على هذه القاعدة دائما ؛ فلا تستطيع البداية بالفعل ، و إلا أصبحت جملتك غير شرعية .
احفظ هذه القاعدة ، و عود نفسك عليها عندما تقرأ أي كلام إنجليزي ؛ فاستخرج الفاعل و الفعل و المفعول به دائما حتى ترسخ في ذهنك ، و عندما تحاول إنشاء جملة إنجليزية من عندك فاعملها على هذا الترتيب الذي تعلمناه : فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به .
و بالطبع هناك بعض الكماليات للجملة ، و لكنها لا تهمك في الوقت الحاضر.
الآن خذ هذه الجمل الإنجليزية ، و استخر الفاعل ، و الفعل ، و المفعول به .
تدريب 1:
Scrooge never painted out Old Marley’s name. There it stood, years afterwards, above the warehouse door: Scrooge and Marley. The firm was known as Scrooge and Marley. Sometimes people new to the business called Scrooge Scrooge, and sometimes Marley, but he answered to both names. It was all the same to him.
و الآن دعنا نعود للدور الأول من البناية التي بنيناها ، و نبدأ معا ؛ نلاحظ أن البسيط أخذ الثلاثة أزمنة ؛ فهناك ماضي بسيط ، و مضارع بسيط ، و مستقبل بسيط ، و البسيط هو - كما يتضح من اسمه - أبسط التراكيب ، و أبعدها عن التعقيد ؛ فهو لا يعتمد على أية أفعال مساعدة.
لنبدأ بالماضي البسيط past simple :
أنا عملت في بنك من عام 1999 إلى عام 2004
هذه الجملة تتكون من : الضمير المنفصل (أنا)
و الفعل بصيغة الماضي (عمل)
و بقية الجملة (في بنك من عام ... إلخ) .
لنحولها إلى اللغة الإنجليزية ، و نستخرج من المستودع الذي رسمناه سابقا ما نريد :
لنذهب أولا إلى قسم (أ) حيث الضمائر المنفصلة ؛ فنجد أن أنا تعني I .
نتوجه ثانيا إلى قسم (ب) حيث تصريف الأفعال (العادية و الشاذة) ، و عمل تعني work و هي من الأفعال العادية أو القياسية ؛ فيكون الماضي البسيط منها أو التصريف الثاني ، و هو ما نستخدمه في زمن الماضي هو: worked
بقية الجملة (في بنك من عام ... إلخ) = in a bank from 1999 to 2004
فلنضع ما بحوزتنا معا :
I worked in a bank from 1999 to 2004
و هذا هو الماضي البسيط ، و تستطيع إضافة زمن لتحديده كما فعلنا ؛ فالماضي البسيط ليس محدد بزمن معين بل يعني فترة سابقة غير محددة ؛ فإذا قلت أنا عملت في بنك I worked in a bank ؛ فهذا له أكثر من احتمال ؛ فقد تكون تقصد البارحة أو قبل خمس سنوات ، و لن يستطيع أحد معرفة الوقت الذي عملت فيه في البنك إلا إذا حددت ذلك .
الخلاصة :
الماضي البسيط يعتمد – ككل الأزمنة القادمة – على تركيب الجملة الإنجليزية ؛ فالجملة الإنجليزية تتكون – كما عرفنا – من فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به . و عندما نريد جعل الجملة في حال الماضي البسيط ؛ فإننا نقوم بتحويل الفعل فقط إلى تصريف الماضي البسيط ، و تبقى الجملة كما هي عليه ، و سيتبين لك الفرق أكثر بعد دراستك لبقية الأزمنة ، و المقارنة بينها ؛ فلا تستعجل .
انتهينا من الشقة الأولى في الدور الأول من بنايتنا ، و هي الماضي البسيط ، و نتوجه الآن إلى جارتها الشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع البسيط.
المضارع البسيط يعني الاستمرار في عمل الشيء ، و ليس استمرار مؤقتا ؛ بل استمرار دائما يوميا أو أسبوعيا أو شهريا . مثال ذلك : أنا أذهب إلى المدرسة كل يوم . I go to school (every day)
فهذا يفيد الاستمرار اليومي للذهاب إلى المدرسة .
وإذا أردنا قاعدته الإنجليزية ؛ فهي أن نأخذ التصريف الأول للفعل الذي سميناه المضارع .
دعونا نأخذ جملة جديدة ، و نشرحها بدلا من جملتنا السابقة ، خذ مثلا :
أحمد يعمل في مكتبة .
لدينا هنا : أحمد – يعمل
أحمد ترجمتها : Ahmed ؛ فهي اسم .
يعمل work
انتبه هنا لشيء يميز المضارع البسيط ، و هو أن الفعل للمفرد يأخذ s بينما الجمع ؛ فيبقى الفعل بصيغته ، و نعني بالمفرد يعمل أو تعمل أما الجمع ؛ فهو يعملون تعملن تعملان .. إلخ .
ولتسهيلها عليك فالفعل الذي يأتي بعد:
He, She, It
يكون مفردا
أما الفعل الذي يأتي بعد:
I, You, They, We
فيكون جمعا .
لعلك تتساءل الآن لماذا أدخلنا I و التي بمعنى "أنا" و You و التي بمعنى "أنت" إلى قائمة الجمع .
حسنا (أنا) و (أنت) تستخدم بصيغة الجمع للمخاطب ؛ فهم يستخدمونها للتفخيم ؛ مثلا عندما تريد أن تفخم المخاطب ، و تقول له: حضرتكم يا سيادة الرئيس كذا و كذا .. فأنت استخدمت الجمع على الرغم من أن الرئيس مفرد ، و لكنك استخدمتها للتفخيم ، و كذا الحال عند الحديث عن نفسك بصيغة الجمع : قرأنا خطابكم الكريم . فأنت تستخدم صيغة الجمع ، و الفرق بين العربية و الإنجليزية أن الإنجليزية تستخدمها دائما بصيغة الجمع أما في العربية ففي بعض الحالات ، و على الرغم من هذا التعليل إلا أنك يجب أن تعرف أن اللغة الإنجليزية لا يشترط أن يكون لها تعليل ؛ بل أحيانا تضطر لأخذ ما فيها بدون تعليل ؛ بل هكذا هم يتحدثون ، و هذه هي قواعدهم ؛ فانتبه أن تبحث دوما عن التفسير أو المقارنة باللغة العربية ؛ فسيدخلك ذلك في حيرة .
نعود لحديثنا عن المضارع البسيط ؛ فهو يعطي :
I, You, They, We
صيغة الفعل الأصلية في التصريف ، مثال:
I go to school every day
We work in a bank
فلاحظ الفعلين : go, work بقيا على حالتها الأصلية وهو التصريف الأول للفعل بدون أي إضافات.
أما في :
He, She, It
فتضيف s على الفعل ، و مثال ذلك :
He goes to school every day
It drinks milk
لاحظ أننا أضفنا إلى الفعلين: go, drink حرف s و ذلك من أجل أنها أتت بعد :
He, she, it
سواء حددت أن ذلك يتم كل يوم أو أسبوع أم لم تحدد ذلك ؛ فعندما تستخدم المضارع البسيط ؛ فسيفهم من كلامك الاستمرارية يوميا أو أسبوعيا .. إلخ ، و أن هذا يحدث بشكل دوري ، و لك الحرية بتحديد ذلك أو جعله مبهما إذا لم يكن مهما ؛ فمثلا عندما تريد أن تخبر أحدا أنك تلعب كرة القدم باستمرار ؛ فستقول :
I play football (soccer)
و سيعلم المستمع أن تلعب كرة القدم باستمرار ، و هذا ما أعطاك لياقة بدنية عالية مثلا ؛ فلا يحتاج أن يعلم الوقت هل هو يومي أم غير ذلك ، و الأمر كله يعود إليك في تحديد ذلك .
في الجملة الأخيرة استخدمنا كلمة Football و Soccer وكلاهما يعني كرة القدم ، و لكن Football مستخدمة في الأمم المتحدة (بريطانيا و أخواتها) أما Soccer فتستخدم في أمريكا ، و لو استخدمت Football في أمريكا فسيظنونك تقصد كرة القدم الأمريكية ، و التي فيها الركل و استخدام الكرة باليد .. إلخ !
و هكذا انهينا من المضارع البسيط ؛ فهو يفيد الاستمرار اليومي الأسبوعي أو حتى كل ساعة ، و لكنه بشكل عام يفيد الاستمرار بأنك تعمل ذلك من وقت لآخر بترتيب معين .
و نضيف S للأفعال المفردة ، و يبقى الفعل بحالته الأصلية لأفعال الجمع .
الخلاصة:
المضارع البسيط يفيد حدوث الشيء بشكل دوري ، يومي .. أسبوعي .. سنوي .. إلخ .
و قاعدته أنك تغير الفعل في الجملة الإنجليزية التي تعلمنا سابقا أركانها الثلاث ؛ فتأخذ الفعل بصيغة المضارع ، و هي التصريف الأول للفعل ، و تضيف إليه حرف s إذا أتى بعد He, she, it ، و لا تضيف له شيئا إذا أتى بعد: I, You, They, We
نذهب الآن للشقة الأخيرة في الدور الأول ، و هي المستقبل البسيط ,
قاعدة المستقبل البسيط كسولة جدا ؛ فهي لا تملك سوى Will و تضيفها لقاعدة المضارع البسيط ، و لكنها لا تعتبر بالجمع أو المفرد فلا تضيف s ؛ بل يبقى الفعل في حالته الأصلية . مثال:
أنا سأذهب إلى المدرسة غدا .
I will go to school tomorrow
هو سيذهب إلى المدرسة غدا
He will go to school tomorrow
لاحظ أننا لم ننظر للفعل هل هو مفرد أم جمع بل أخذناه بصيغته الأصلية في التصريف ، و أضفنا قبله كلمة Will و التي تعني سوف ، و انتهينا .
أما ما يفيد به المستقبل البسيط ؛ فهو الحديث عن المستقبل بشكل مبهم أيضا ، و تستطيع تحديد ذلك أو تجاهله كما سبق الحديث عن ذلك في المضارع البسيط ؛ فتستطيع القول: أنا سأسافر غدا أو أنا سأسافر . و اختيارك للألفاظ يعتمد على حاجة المتلقي .
أمثلة:
أنا سأجتهد في الامتحان .
I will work hard in the exam
هو سيجتهد في الامتحان
He will work hard in the exam
الخلاصة: المستقبل البسيط يأخذ الفعل بحالته الأصلية أو التصريف الأول (المضارع) له ، و يضيف قبل ذلك Will فقط بغض النظر عن نوع الفاعل قبله ؛ فكل الضمائر : I, You, They, We, He, she, it يأتي بعدها will ثم الفعل بتصريفه الأول دون أن نضيف s على أي منها . ويفيد المستقبل البسيط بالإخبار عن حدث سيكون في المستقبل ، و لكن بشكل مبهم و دون معرفة وقته المحدد ، و يعود إليك تحديد الوقت .
انتهينا من الأزمنة البسيطة ، و هي الماضي البسيط ، و المضارع البسيط ، و المستقبل البسيط .
تدريب 2:
حدد نوع الجملة ، و من أي الأزمنة هي ، ثم حولها إلى الزمنين البسيطين الآخرين:
We had the carriage
He cleaned his teeth
It will rain tomorrow
They play tennis
You will watch television
She speaks Spanish
مثال للحل:
We had the carriage
زمن الجملة: ماضي بسيط
تحويلها إلى:
المضارع البسيط:
We have the carriage
المستقبل البسيط:
We will have the carriage
انتهى الدور الأول كاملا .
منقووول
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
انتهينا من الدور الأول كاملا ، و الذي احتوى الزمن الماضي و المضارع و المستقبل البسيط ، نصعد الآن إلى الدور الثاني من بنايتنا ، و هو المستمر .. اممم ! لقد مر علينا كلمة المستمر سابقا أو كلمة الاستمرارية في المضارع البسيط ، و هي تفيد أن ذلك العمل يتم يوميا أو أسبوعيا مثلا ؛ فما الفرق بين ذلك ، و بين هذا الدور الذي أسميناه المستمر ؛ فهناك ماضي مستمر ، و مضارع و مستقبل مستمرين .
حسنا .. الاستمرار هنا يختلف عن ذلك ؛ فهذا الاستمرار يعني فترة معينة من الوقت ؛ مثلا من الساعة الرابعة إلى الخامسة عصرا فقط ، و ينتهي الفعل ؛ فأنا لا أمارسه كل يوم بل مارسته مرة واحدة لمدة من الوقت سواء كانت بالساعات أو حتى بالأيام .
لأوضح ذلك أكثر بالمثال :
أنا ألعب كرة القدم.
أنا ألعب كرة القدم.
هل تلاحظ الفرق بينهما ؟!
حسنا .. دعنا نكتبهما باللغة الإنجليزية :
I play football
I am playing football
أوه ! لقد اختلفت الجملتان الآن ! ألم أخبرك ألا تحاول مقارنة العربية بالإنجليزية ؛ بل يجب أن تأخذ الإنجليزية بتفكيرها و قواعدها بعيدا عن مقارنتها بالعربية ؛ فهم يجعلون قواعد للحديث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار و بشكل دوري يومي أو أسبوعي ، و يجعلون قواعد أخرى للحديث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار لفترة معينة ثم يتوقف .
والآن دعنا نتحدث عن المضارع المستمر ، و هو present continuous :
الساعة الآن الرابعة عصرا ، و أنت تلعب كرة القدم ، و أنا اتصلت بك ، و سألت: ماذا تفعل ؟ تجيبني : أنا ألعب كرة القدم .
حسنا .. عندما أخبرتني أنك تلعب كرة القدم ؛ فأنت تقصد الآن في هذا الوقت ، وحتى تنتهي منها بعد نصف ساعة مثلا ، و بعد ذلك قد تلعبها و قد لا تلعبها . المهم أنك تتحدث عما يجري الآن ، و هذا هو المضارع المستمر أو present continuous ؛ فهو الحديث عما يجري حاليا .
أما المضارع البسيط أو present simple ؛ فأنت تتحدث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار كالذهاب إلى العمل أو المدرسة ؛ فأنت تذهب يوميا .
الآن دعني أصعبها عليك ، و ألخبط فهمك لها ، ترجم لي هذه الجملة إلى الإنجليزية :
أنا أعمل على هذه الملفات منذ يومين .
دعنا من هذا فأنت الآن فهمت الفرق بينهما ، و لكن عقلك سيرفض التصديق بذلك ؛ لأنه تعود على قواعد اللغة العربية ، و يحاول تطبيق كل قاعدة جديدة على القواعد القديمة ، و لذلك عليك إجباره على التفريق بينهما و أنها قاعدة جديدة لا علاقة لها بقواعد اللغة العربية ، و لن يقتنع عقلك إلا بعد الاستمرار و المداومة على مراجعة هذه القواعد و حفظها ؛ فسيقتنع أخيرا ، و يجعل لها مكانا جديدا و خاصا بها .
بعد أن فهمت الفرق في أنواع الاستمرارية ؛ دعنا نعود إلى الشقة الثانية وليست الأولى من الدور الثاني من بنايتنا ، فبالدور الثاني كما تعرف يحتوي على الشقة الأولى و هي الماضي المستمر ثم الشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع المستمر ثم الشقة الثالثة ، و هي المستقبل المستمر . و لنبدأ بالشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع المستمر ؛ فلديها المفاتيح لسائر الشقق ، و عند فهمها ستستطيع المرور على الشقق الأخرى بسهولة .
قاعدة المضارع المستمر:
تبدأ أولا بالفاعل أو بالضمير: I. He, They.. إلخ ، أو بالاسم أحمد ، حصه
و بعد ذلك تأتي بالفعل المساعد am, is, are
و بعد ذلك الفعل في حالته الأصلية ، و تضيف إليه ing .
هناك شيء جديد ظهر لنا ، و هو الفعل المساعد أما بالنسبة لـ ing فهي قاعدة المستمر الماضي و المضارع و المستقبل ؛ فخذها كما هي .
الفعل المساعد هو فعل حقيقي له تصريفاته الثلاث ، و لكنه ينزل متطوعا و متكرما ليكون رابطا بين الضمير I. He, .. إلخ ، و الفعل المضاف إليه ing .
اممم ! يبدو أنك لاحظت أن هناك العديد من المشاكل في الجملة الإنجليزية ؛ فالضمير لا يقبل الاتصال بالفعل المضاف إليه ing ؛ و يحتاج لأهل الخير أن يتدخلوا . و الفعل المساعد هو من أهل الخير ، و لكنه لا يرضى أن تقلل من احترامه ، و تأتي به مع فعل آخر .
دعني أشرح لك قليلا ؛ فقد عرفنا تركيب الجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و هو: فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به.
حسنا .. انظر لهذه الجملة:
أحمد يلعب كرة القدم
تحتوي هذه الجملة على ثلاثة أشياء :
أحمد و ترجمتها حرفيا Ahmed
يلعب و ترجمتها حرفيا Play
كرة القدم و ترجمتها حرفيا Football
في القواعد يكون عملنا على منطقة الفعل ؛ فهو من يتحكم بالجملة ، و يحدث تغييرات جذرية عليها ، و يؤثر على المفعول به أما الفاعل فيبقى على حاله .
إذن أحمد تبقى على حالها .
Play فعل في التصريف الأول ، و نريد تحويله للاستمرارية الوقتية يعني من الساعة الرابعة إلى الخامسة عصرا مثلا ؛ فنحتاج لإضافة ing إلى الفعل ليصبح مستمرا .
و لكن هنا تبرز لنا مشكلة ؛ فلو عدنا إلى بداية الموضوع ، و بحثنا في المستودع الذي أنشأناه بجوار البناية لوجدنا أن الأفعال لها ثلاث تصريفات :
infinitive و تعني الفعل في حالته الأصلية أو سمه المضارع .
past simple تعني صيغة الماضي البسيط للفعل .
past participle تعني التصريف الثالث للفعل .
و مثالها على go :
Go – went – gone
وكذلك:
Play – played – played
عندما أضفنا ing إلى الفعل play ؛ هل أصبح يشبه أي من تصريفاته السابقة ؟ الجواب: لا ! إذن لم يعد لدينا فعل تقوم به الجملة ، و أصبح معنى playing هو لاعب و ليس يلعب !
اختل تركيب الجملة الإنجليزية عندما أضفنا ing ، و لم يعد لدينا فعل ، و الفعل كما تعرف هو الركن الثاني من تركيب الجملة.
اممم ! ما لحل إذن ؟!
هنا يبرز دور الفعل be و أبناءه am. is, are . دعوني أحدثكم عن الفعل be وما قصته ..
كان الفعل be جالسا مع بقية الأفعال في أمان الله ، و من حيث لم يشعر أنجب له ثلاثة أبناء و هم am, is, are ، وهو و أبناؤه أصبحوا التصريف الأول ، وحتى لا يكون هناك ازدواجية في الأدوار كان بينهم تفاهم ؛ فأحيانا يقوم الأولاد متفرقين بأداء بعض المهام المحددة عن والدهم ، و أحيانا يقوم الأب بتنفيذ المهمة بنفسه . إذن التصريف الأول لـ be يشمل أربعة أفعال دفعة واحدة ، و لكن بينهم تفاهم . و أيضا في التصريف الثاني لهم و هو ما يفترض أن يكون الماضي البسيط أنجبوا فعلين يستقران هناك ، و هما was, were ، أما التصريف الثالث ؛ فالجد هو been
شكل 6
إذن أمامنا عائلة كاملة سببت زحاما و ربكة بين الأفعال ؛ فقد خلفت أبناء ، و انتشرت فروعها ، و لكنها عزمت التكفير عن خطيئتها بمساعدة الجمل التي تحتاج لأفعال ؛ فأرضت الجميع ، و ينبغي أن تعرف أن be تعني (يكون) ، و هذه كلمة فضفاضة تستطيع وضعها في أي مكان ؛ فتستطيع أن تقول: أنا أكون مدرس ، و تستطيع أن تستغني عنها في اللغة العربية ؛ فتقول أنا مدرس ؛ فاللغة العربية لا تحتاج لفعل بعكس اللغة الإنجليزية التي عندما تورطت أنقذتها عائلة الفعل be من حيرتها ، و لكن ينبغي أن تعلم أن الفعل be و مشتقاته – على الرغم أنهم تطوعوا للخدمة – إلا أنهم لا يرضون أبدا أن يكون هناك فعل في الجملة معهم ؛ فلا تستطيع أن تقول في اللغة الإنجليزية : I am play football ؛ و إلا سببت مشكلة رهيبة و حربا بين الأفعال ؛ فلكل فعل جملته الخاصة به ، و أرجوك .. لا تضع فعلا مع فعل آخر .
علمت الآن ما هو دور الفعل be وعائلته الكريمة ، و أنهم ينقذون الجملة الإنجليزية ، و يحافظون على قاعدتها الثابتة : فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به.
نعود للمضارع المستمر ؛ فإذا أردت أن تقول : أنا ألعب كرة القدم الآن .
فتأتي بالفاعل الذي هو أنا و تعني : I
ثم بالفعل ، و بما أن الفعل يلعب تغير و لم يعد فعلا بل أصبح مفعولا به ؛ فنستعين بعائلة be التي تسعفنا ، و تعطينا am حصريا للفاعل I
ثم بالمفعول به الذي هو لاعب كرة القدم playing football now
فتصبح الجملة :
I am playing football now
تذكر أنه عندما أضفنا ing للفعل تغير ، و أصبح مفعولا به ؛ فاضطررنا لجلب فعل آخر و هو من عائلة be التي تطوعت لهذا العمل ؛ فأصبحت تسمى الأفعال المساعدة .
و كما قلنا أن عائلة be أو الأفعال المساعدة لها مهامها المحددة ، و انظر الجدول التالي يبين لك مهامها بالتحديد:
شكل 7

لاحظ أن am محصورة في I للمضارع
أما was فهي مشتركة بين I, He, She, It في الماضي
و الآن دعونا نترجم هذه الجمل:
أنا أكتب رسالة الآن .
هو يحمل كتابا معه الآن .
هم يركضون بسرعة الآن.
انتهت الأمثلة ، و لاحظ أننا نقول : الآن ، و هذا في اللغة العربية فقط ؛ أما في الإنجليزية ؛ فلا تحتاج لذلك ؛ لأن الجملة تفيد ذلك المعنى ؛ فعندما تستخدم المضارع المستمر ؛ فأنت تتحدث عن الوقت الحالي .
وبهذا ننتهي من المضارع المستمر ، و هو الشقة الثانية من الدور الثاني من بنايتنا .
ماذا ؟! تريدون الحلول للأمثلة .. اممم ! حسنا إليكم الحلول ، و يجب أن تكونوا قد حاولتم بأنفسكم قبل الاطلاع عليها :
I am writing a letter
He is carrying a book
They are running fast.
الخلاصة: المضارع المستمر يفيد استمرارية الفعل الوقتية و ينتهي بعدها ؛ فأنت تلعب كرة القدم في العصر لمدة نصف ساعة ، و بعد ذلك تتوقف ففترة لعبك و هي النصف ساعة ؛ هي المضارع المستمر . أما قاعدة المضارع المستمر ؛ فهي أن يبقى الفاعل كما هو من دون تغيير ثم نأتي بفعل مساعد من عائلة be ، و بعد ذلك المفعول به وهو الفعل الذي أضفنا إليه ing وبقية الجملة.
نتوجه الآن إلى الشقة الأولى و هي الماضي المستمر :
لو أردنا أن نحول المضارع المستمر للماضي المستمر ، و مثال ذلك : أنا كنت ألعب كرة القدم قبل قليل.
فكل ما علينا هو تحويل الفعل المساعد الذي من عائلة be كما علمنا إلى التصريف الماضي .
أنا ألعب كرة القدم è مضارع مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية
أنا كنت ألعب كرة القدم è ماضي مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية
تعرفنا في الجدول السابق على تصريف am في الماضي و هو was ؛ إذن علينا استبدالها فقط .
I was playing football
He was playing football
They were playing football
اممم ! ألم أخبركم أنه عندما تفهم المضارع المستمر ، و هو الشقة الثانية ؛ فسيعطيك المفاتيح لسائر الأبواب !
الشقة الثالثة ، و هي المستقبل المستمر:
استمعوا إلى هذه المحادثة:
-أين أنت يا أحمد ؟
-أنا أستعد للعب كرة القدم .
-حسنا .. سأتصل عليك بعد عشر دقائق !
-كلا .. فأنا سأكون ألعب كرة القدم وقتها è مستقبل مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية .
برأيي أن الزمن المستمر هو أسهل الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و عندما تفهمه جيدا فستحبه كثيرا ، و تكتشف أشياء مثيرة به .
بقي لدينا قاعدة المستقبل المستمر ، حسنا .. كما قلنا سابقا ؛ فالمستقبل هو زمن كسول في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و كل ما يفعله أن يعيد الفعل إلى حالته الأصلية ، و يضيف will قبله ، و لا يسمح بأي تشعبات .
فنحن في المضارع المستمر ، وزعنا am, is, are بين I, he, she, it, they, you, we ، و بما أن المستقبل زمن كسول ؛ فهو يريد إعادة كل شيء على طبيعته ؛ فلا يستطيع العمل بكل هذا التشعبات ؛ فهل تعلمون ما هو الحل الذي خرج به ؟!
Be
نعم .. لقد اعتمد على الأب فقط ، و ترك الأولاد am, is, are يلعبون بعيدا عنه ؛ فصارت قاعدته:
الفاعل ، و هو الضمير I أو الاسم .
Will تسبق الفعل
الفعل بحالته الأصلية ، و هنا يأخذ be ؛ لأننا نستخدم أفعال مساعدة
المفعول به و هو الفعل الذي أضفنا له Ing فأصبح مفعولا به.
مثال:
أنا سأكون لاعبا كرة القدم بعد قليل
I will be playing football
لاحظ أنني عند الترجمة أحذف الكلمات التي تدل على الزمن (الآن – بعد قليل) ، و ذلك لأنك تستطيع الاستغناء عنها في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ لأن الجملة تدل على ذلك .
و الحظ أيضا أن صيغة الجملة في اللغة العربية غير صحيحة تماما ؛ بل هي للتوضيح ، و نستطيع أن نقول: أن سألعب كرة القدم ؛ فالمضارع في اللغة العربية يشمل الكثير من الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية.
انتهينا من الدور الثاني كاملا كما انتهينا سابقا من الدور الأول .
تذكرت شيئا مهما ، و هو ألا تحاول الصعود لكل الأدوار معا ، بل خصص يومين مثلا للدور الأول ، و بعد ذلك انتقل للدور الثاني ، ثم الثالث .
و إذا أحسست بصعوبة في ذلك ؛ فخذ شقة واحدة لكل يوم أو يومين . المهم ألا تحاول المرور السريع على الأدوار ؛ فهذا سيتعبك ، و قد تضيع معلوماتك الأولى .
انتهى الدور الثاني كاملا
حسنا .. الاستمرار هنا يختلف عن ذلك ؛ فهذا الاستمرار يعني فترة معينة من الوقت ؛ مثلا من الساعة الرابعة إلى الخامسة عصرا فقط ، و ينتهي الفعل ؛ فأنا لا أمارسه كل يوم بل مارسته مرة واحدة لمدة من الوقت سواء كانت بالساعات أو حتى بالأيام .
لأوضح ذلك أكثر بالمثال :
أنا ألعب كرة القدم.
أنا ألعب كرة القدم.
هل تلاحظ الفرق بينهما ؟!
حسنا .. دعنا نكتبهما باللغة الإنجليزية :
I play football
I am playing football
أوه ! لقد اختلفت الجملتان الآن ! ألم أخبرك ألا تحاول مقارنة العربية بالإنجليزية ؛ بل يجب أن تأخذ الإنجليزية بتفكيرها و قواعدها بعيدا عن مقارنتها بالعربية ؛ فهم يجعلون قواعد للحديث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار و بشكل دوري يومي أو أسبوعي ، و يجعلون قواعد أخرى للحديث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار لفترة معينة ثم يتوقف .
والآن دعنا نتحدث عن المضارع المستمر ، و هو present continuous :
الساعة الآن الرابعة عصرا ، و أنت تلعب كرة القدم ، و أنا اتصلت بك ، و سألت: ماذا تفعل ؟ تجيبني : أنا ألعب كرة القدم .
حسنا .. عندما أخبرتني أنك تلعب كرة القدم ؛ فأنت تقصد الآن في هذا الوقت ، وحتى تنتهي منها بعد نصف ساعة مثلا ، و بعد ذلك قد تلعبها و قد لا تلعبها . المهم أنك تتحدث عما يجري الآن ، و هذا هو المضارع المستمر أو present continuous ؛ فهو الحديث عما يجري حاليا .
أما المضارع البسيط أو present simple ؛ فأنت تتحدث عن شيء يحدث باستمرار كالذهاب إلى العمل أو المدرسة ؛ فأنت تذهب يوميا .
الآن دعني أصعبها عليك ، و ألخبط فهمك لها ، ترجم لي هذه الجملة إلى الإنجليزية :
أنا أعمل على هذه الملفات منذ يومين .
دعنا من هذا فأنت الآن فهمت الفرق بينهما ، و لكن عقلك سيرفض التصديق بذلك ؛ لأنه تعود على قواعد اللغة العربية ، و يحاول تطبيق كل قاعدة جديدة على القواعد القديمة ، و لذلك عليك إجباره على التفريق بينهما و أنها قاعدة جديدة لا علاقة لها بقواعد اللغة العربية ، و لن يقتنع عقلك إلا بعد الاستمرار و المداومة على مراجعة هذه القواعد و حفظها ؛ فسيقتنع أخيرا ، و يجعل لها مكانا جديدا و خاصا بها .
بعد أن فهمت الفرق في أنواع الاستمرارية ؛ دعنا نعود إلى الشقة الثانية وليست الأولى من الدور الثاني من بنايتنا ، فبالدور الثاني كما تعرف يحتوي على الشقة الأولى و هي الماضي المستمر ثم الشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع المستمر ثم الشقة الثالثة ، و هي المستقبل المستمر . و لنبدأ بالشقة الثانية ، و هي المضارع المستمر ؛ فلديها المفاتيح لسائر الشقق ، و عند فهمها ستستطيع المرور على الشقق الأخرى بسهولة .
قاعدة المضارع المستمر:
تبدأ أولا بالفاعل أو بالضمير: I. He, They.. إلخ ، أو بالاسم أحمد ، حصه
و بعد ذلك تأتي بالفعل المساعد am, is, are
و بعد ذلك الفعل في حالته الأصلية ، و تضيف إليه ing .
هناك شيء جديد ظهر لنا ، و هو الفعل المساعد أما بالنسبة لـ ing فهي قاعدة المستمر الماضي و المضارع و المستقبل ؛ فخذها كما هي .
الفعل المساعد هو فعل حقيقي له تصريفاته الثلاث ، و لكنه ينزل متطوعا و متكرما ليكون رابطا بين الضمير I. He, .. إلخ ، و الفعل المضاف إليه ing .
اممم ! يبدو أنك لاحظت أن هناك العديد من المشاكل في الجملة الإنجليزية ؛ فالضمير لا يقبل الاتصال بالفعل المضاف إليه ing ؛ و يحتاج لأهل الخير أن يتدخلوا . و الفعل المساعد هو من أهل الخير ، و لكنه لا يرضى أن تقلل من احترامه ، و تأتي به مع فعل آخر .
دعني أشرح لك قليلا ؛ فقد عرفنا تركيب الجملة في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و هو: فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به.
حسنا .. انظر لهذه الجملة:
أحمد يلعب كرة القدم
تحتوي هذه الجملة على ثلاثة أشياء :
أحمد و ترجمتها حرفيا Ahmed
يلعب و ترجمتها حرفيا Play
كرة القدم و ترجمتها حرفيا Football
في القواعد يكون عملنا على منطقة الفعل ؛ فهو من يتحكم بالجملة ، و يحدث تغييرات جذرية عليها ، و يؤثر على المفعول به أما الفاعل فيبقى على حاله .
إذن أحمد تبقى على حالها .
Play فعل في التصريف الأول ، و نريد تحويله للاستمرارية الوقتية يعني من الساعة الرابعة إلى الخامسة عصرا مثلا ؛ فنحتاج لإضافة ing إلى الفعل ليصبح مستمرا .
و لكن هنا تبرز لنا مشكلة ؛ فلو عدنا إلى بداية الموضوع ، و بحثنا في المستودع الذي أنشأناه بجوار البناية لوجدنا أن الأفعال لها ثلاث تصريفات :
infinitive و تعني الفعل في حالته الأصلية أو سمه المضارع .
past simple تعني صيغة الماضي البسيط للفعل .
past participle تعني التصريف الثالث للفعل .
و مثالها على go :
Go – went – gone
وكذلك:
Play – played – played
عندما أضفنا ing إلى الفعل play ؛ هل أصبح يشبه أي من تصريفاته السابقة ؟ الجواب: لا ! إذن لم يعد لدينا فعل تقوم به الجملة ، و أصبح معنى playing هو لاعب و ليس يلعب !
اختل تركيب الجملة الإنجليزية عندما أضفنا ing ، و لم يعد لدينا فعل ، و الفعل كما تعرف هو الركن الثاني من تركيب الجملة.
اممم ! ما لحل إذن ؟!
هنا يبرز دور الفعل be و أبناءه am. is, are . دعوني أحدثكم عن الفعل be وما قصته ..
كان الفعل be جالسا مع بقية الأفعال في أمان الله ، و من حيث لم يشعر أنجب له ثلاثة أبناء و هم am, is, are ، وهو و أبناؤه أصبحوا التصريف الأول ، وحتى لا يكون هناك ازدواجية في الأدوار كان بينهم تفاهم ؛ فأحيانا يقوم الأولاد متفرقين بأداء بعض المهام المحددة عن والدهم ، و أحيانا يقوم الأب بتنفيذ المهمة بنفسه . إذن التصريف الأول لـ be يشمل أربعة أفعال دفعة واحدة ، و لكن بينهم تفاهم . و أيضا في التصريف الثاني لهم و هو ما يفترض أن يكون الماضي البسيط أنجبوا فعلين يستقران هناك ، و هما was, were ، أما التصريف الثالث ؛ فالجد هو been
شكل 6
إذن أمامنا عائلة كاملة سببت زحاما و ربكة بين الأفعال ؛ فقد خلفت أبناء ، و انتشرت فروعها ، و لكنها عزمت التكفير عن خطيئتها بمساعدة الجمل التي تحتاج لأفعال ؛ فأرضت الجميع ، و ينبغي أن تعرف أن be تعني (يكون) ، و هذه كلمة فضفاضة تستطيع وضعها في أي مكان ؛ فتستطيع أن تقول: أنا أكون مدرس ، و تستطيع أن تستغني عنها في اللغة العربية ؛ فتقول أنا مدرس ؛ فاللغة العربية لا تحتاج لفعل بعكس اللغة الإنجليزية التي عندما تورطت أنقذتها عائلة الفعل be من حيرتها ، و لكن ينبغي أن تعلم أن الفعل be و مشتقاته – على الرغم أنهم تطوعوا للخدمة – إلا أنهم لا يرضون أبدا أن يكون هناك فعل في الجملة معهم ؛ فلا تستطيع أن تقول في اللغة الإنجليزية : I am play football ؛ و إلا سببت مشكلة رهيبة و حربا بين الأفعال ؛ فلكل فعل جملته الخاصة به ، و أرجوك .. لا تضع فعلا مع فعل آخر .
علمت الآن ما هو دور الفعل be وعائلته الكريمة ، و أنهم ينقذون الجملة الإنجليزية ، و يحافظون على قاعدتها الثابتة : فاعل ثم فعل ثم مفعول به.
نعود للمضارع المستمر ؛ فإذا أردت أن تقول : أنا ألعب كرة القدم الآن .
فتأتي بالفاعل الذي هو أنا و تعني : I
ثم بالفعل ، و بما أن الفعل يلعب تغير و لم يعد فعلا بل أصبح مفعولا به ؛ فنستعين بعائلة be التي تسعفنا ، و تعطينا am حصريا للفاعل I
ثم بالمفعول به الذي هو لاعب كرة القدم playing football now
فتصبح الجملة :
I am playing football now
تذكر أنه عندما أضفنا ing للفعل تغير ، و أصبح مفعولا به ؛ فاضطررنا لجلب فعل آخر و هو من عائلة be التي تطوعت لهذا العمل ؛ فأصبحت تسمى الأفعال المساعدة .
و كما قلنا أن عائلة be أو الأفعال المساعدة لها مهامها المحددة ، و انظر الجدول التالي يبين لك مهامها بالتحديد:
شكل 7

لاحظ أن am محصورة في I للمضارع
أما was فهي مشتركة بين I, He, She, It في الماضي
و الآن دعونا نترجم هذه الجمل:
أنا أكتب رسالة الآن .
هو يحمل كتابا معه الآن .
هم يركضون بسرعة الآن.
انتهت الأمثلة ، و لاحظ أننا نقول : الآن ، و هذا في اللغة العربية فقط ؛ أما في الإنجليزية ؛ فلا تحتاج لذلك ؛ لأن الجملة تفيد ذلك المعنى ؛ فعندما تستخدم المضارع المستمر ؛ فأنت تتحدث عن الوقت الحالي .
وبهذا ننتهي من المضارع المستمر ، و هو الشقة الثانية من الدور الثاني من بنايتنا .
ماذا ؟! تريدون الحلول للأمثلة .. اممم ! حسنا إليكم الحلول ، و يجب أن تكونوا قد حاولتم بأنفسكم قبل الاطلاع عليها :
I am writing a letter
He is carrying a book
They are running fast.
الخلاصة: المضارع المستمر يفيد استمرارية الفعل الوقتية و ينتهي بعدها ؛ فأنت تلعب كرة القدم في العصر لمدة نصف ساعة ، و بعد ذلك تتوقف ففترة لعبك و هي النصف ساعة ؛ هي المضارع المستمر . أما قاعدة المضارع المستمر ؛ فهي أن يبقى الفاعل كما هو من دون تغيير ثم نأتي بفعل مساعد من عائلة be ، و بعد ذلك المفعول به وهو الفعل الذي أضفنا إليه ing وبقية الجملة.
نتوجه الآن إلى الشقة الأولى و هي الماضي المستمر :
لو أردنا أن نحول المضارع المستمر للماضي المستمر ، و مثال ذلك : أنا كنت ألعب كرة القدم قبل قليل.
فكل ما علينا هو تحويل الفعل المساعد الذي من عائلة be كما علمنا إلى التصريف الماضي .
أنا ألعب كرة القدم è مضارع مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية
أنا كنت ألعب كرة القدم è ماضي مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية
تعرفنا في الجدول السابق على تصريف am في الماضي و هو was ؛ إذن علينا استبدالها فقط .
I was playing football
He was playing football
They were playing football
اممم ! ألم أخبركم أنه عندما تفهم المضارع المستمر ، و هو الشقة الثانية ؛ فسيعطيك المفاتيح لسائر الأبواب !
الشقة الثالثة ، و هي المستقبل المستمر:
استمعوا إلى هذه المحادثة:
-أين أنت يا أحمد ؟
-أنا أستعد للعب كرة القدم .
-حسنا .. سأتصل عليك بعد عشر دقائق !
-كلا .. فأنا سأكون ألعب كرة القدم وقتها è مستقبل مستمر في اللغة الإنجليزية .
برأيي أن الزمن المستمر هو أسهل الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و عندما تفهمه جيدا فستحبه كثيرا ، و تكتشف أشياء مثيرة به .
بقي لدينا قاعدة المستقبل المستمر ، حسنا .. كما قلنا سابقا ؛ فالمستقبل هو زمن كسول في اللغة الإنجليزية ، و كل ما يفعله أن يعيد الفعل إلى حالته الأصلية ، و يضيف will قبله ، و لا يسمح بأي تشعبات .
فنحن في المضارع المستمر ، وزعنا am, is, are بين I, he, she, it, they, you, we ، و بما أن المستقبل زمن كسول ؛ فهو يريد إعادة كل شيء على طبيعته ؛ فلا يستطيع العمل بكل هذا التشعبات ؛ فهل تعلمون ما هو الحل الذي خرج به ؟!
Be
نعم .. لقد اعتمد على الأب فقط ، و ترك الأولاد am, is, are يلعبون بعيدا عنه ؛ فصارت قاعدته:
الفاعل ، و هو الضمير I أو الاسم .
Will تسبق الفعل
الفعل بحالته الأصلية ، و هنا يأخذ be ؛ لأننا نستخدم أفعال مساعدة
المفعول به و هو الفعل الذي أضفنا له Ing فأصبح مفعولا به.
مثال:
أنا سأكون لاعبا كرة القدم بعد قليل
I will be playing football
لاحظ أنني عند الترجمة أحذف الكلمات التي تدل على الزمن (الآن – بعد قليل) ، و ذلك لأنك تستطيع الاستغناء عنها في اللغة الإنجليزية ؛ لأن الجملة تدل على ذلك .
و الحظ أيضا أن صيغة الجملة في اللغة العربية غير صحيحة تماما ؛ بل هي للتوضيح ، و نستطيع أن نقول: أن سألعب كرة القدم ؛ فالمضارع في اللغة العربية يشمل الكثير من الأزمنة في اللغة الإنجليزية.
انتهينا من الدور الثاني كاملا كما انتهينا سابقا من الدور الأول .
تذكرت شيئا مهما ، و هو ألا تحاول الصعود لكل الأدوار معا ، بل خصص يومين مثلا للدور الأول ، و بعد ذلك انتقل للدور الثاني ، ثم الثالث .
و إذا أحسست بصعوبة في ذلك ؛ فخذ شقة واحدة لكل يوم أو يومين . المهم ألا تحاول المرور السريع على الأدوار ؛ فهذا سيتعبك ، و قد تضيع معلوماتك الأولى .
انتهى الدور الثاني كاملا
البطريقة البردانة
New member
رد: اللي محتاسه بالنجليزي ويا عيالها ادش&&&&&
صح كلامج بس شفيه تيلي تبيز ؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟
أهوا وايد مليق بس شفيه..اتذكر كانو مسويين عليه ضجه و أولياء أمور طلعوا إتصامات بلندن بس ما أدري ليش؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟:eh_s(20):
اايد
والاحلا مو افلام كبار
بارني
دورا
مانصح بالتيلي توبيز
صح كلامج بس شفيه تيلي تبيز ؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟
أهوا وايد مليق بس شفيه..اتذكر كانو مسويين عليه ضجه و أولياء أمور طلعوا إتصامات بلندن بس ما أدري ليش؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟:eh_s(20):
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
رد : اللي محتاسه بالنجليزي ويا عيالها ادش&&&&& متجدد **
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
like
We
like
Second Person
You
like
You
like
Third Person
He/she/it
likes
they
like
Present tense forms of have
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
have
We
have
Second Person
You
have
You
have
Third Person
He/she/it
has
they
have
Present tense form of do
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
Do/don’t
We
Do/don’t
Second Person
You
Do/don’t
You
Do/don’t
Third Person
He/she/it
Does/doesn’t
they
Do/don’t
Present tense forms of be
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
am
We
are
Second Person
You
are
You
are
Third Person
He/she/it
is
they
are
Past tense forms of be
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
was
We
were
Second Person
You
were
You
were
Third Person
He/she/it
was
they
were
1- نستخدم الماضي البسيط لنتحدث عن شيء ( حدث ) حصل و انتهى في الماضي في زمن محدد.
مثلا: Last week, I played football.
[COLOR=window****]2- ملاحظة: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****]بعض الكلمات تدل على أن الجملة في الماضي البسيط: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****]yesterday -ago -last...[/COLOR][COLOR=window****][/COLOR]
3- يوضع الفعل في زمن الماضي البسيط في التصريف الثاني بإضافة ed إلى آخر الفعل إذا كان الفعل منتظما أو على حسب
تصريفه إذا كان الفعل غير منتظم
4- يتكون النفي في الماضي البسيط بإضافة كلمة didn't قبل الفعل و يوضع الفعل في التصريف الأول
5- عند تكوين السؤال في الماضي البسيط نضع الفعل المساعد did قبل الفاعل و نضع الفعل في التصريف الأول بعد الفاعل.
6- عند الإجابة على سؤال معلومات يبدأ wh-word نقوم بحذف أداة الإستفهام و نحذف الفعل المساعد did ثم نبدأ بالفاعل و نضع الفعل في التصريف الثاني ثم نذكر الإجابة.
1- يستخدم زمن المضارع البسيط لوصف أ- حقيقة ب- حدث يقع يوميا أو بصفة مكررة ج- عمل
3- يوضع الفعل في زمن المضارع البسيط في التصريف الأول و بإضافة s إلى آخر الفعل
4- يتم نفي الفعل في زمن المضارع البسيط باستخدام الفعل المساعد do / does ثم بإضافة not و حذف s من الفعل.
مثلا:
2- بعض الكلمات تستخدم مع زمن المستقبل مثل next – tomorrow - in the future
3- هناك ثلاث طرق للتحدث عن المستقبل:
أولا : باستخدام will و نضع الفعل في التصريف الأول
ب- تكوين السؤال نضع will قبل الفاعل
He will see you next week. جملة
Will he see you next week ? سؤال بنعم أو لا
When will he see you? سؤال معلومات
ج- عند الإجابة على سؤال معلومات يبدأ wh-word نقوم بحذف أداة الاستفهام و نضع will بعد الفاعل ثم نذكر
الإجابة.
ثانيا: باستخدام going to :
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم going to ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
ثانيا: باستخدام الفعل + am / is / are + الفعل + ing :
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول مضافا إليه -ing
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
2- بعض الكلمات تستخدم مع المضارع المستمر مثل now – right now - at the moment
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول مضافا إليه -ing
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
1- تذكر الصفة بعد الفعل. و الصفات مثل
The restaurant is nice. The food is delicious. 2- يمكن أن يأتي الموصوف ( الاسم ) بعد الصفة و في هذه الحالة نضع قبل الصفة a إذا كان الموصوف مفردا معدودا مثل
و لا نضع a إذا كان الموصوف جمعا أو غير معدود. مثل
1- جداً( very ) و جداً جداً مع الاستحالة ( too )
تستخدم very مع الصفة فتجعل الصفة أقوى و تستخدم ( too ) مع الصفة فتفيد أن هذا الشيء أو الكمية أو الدرجة أكثر مما هو مطلوب أو مقبول ,
من التراكيب التي تستخدم في الكتابة المصدر + to …
TAKE AWAY
Present Tense forms of Like (a typical verb)
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
like
We
like
Second Person
You
like
You
like
Third Person
He/she/it
likes
they
like
Present tense forms of have
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
have
We
have
Second Person
You
have
You
have
Third Person
He/she/it
has
they
have
Present tense form of do
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
Do/don’t
We
Do/don’t
Second Person
You
Do/don’t
You
Do/don’t
Third Person
He/she/it
Does/doesn’t
they
Do/don’t
Present tense forms of be
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
am
We
are
Second Person
You
are
You
are
Third Person
He/she/it
is
they
are
Past tense forms of be
Singular
Plural
First Person
I
was
We
were
Second Person
You
were
You
were
Third Person
He/she/it
was
they
were
TENSE
POSITIVE
NEGATIVE
QUESTION
Simple Present
I play tennis on Mondays.
They don't (do not) work in New York.
Does she know him?
Simple Past
She went to Paris last week.
They didn't (did not) drive to work.
Where did she get that hat?
Simple Future
I'll (will) meet you at the airport tomorrow.
He won't (will not) be able to come.
Will they visit us soon?
Present Continuous
He's (is) working at the moment.
They aren't (are not) coming this evening.
What are you doing?
Past Continuous
I was watching TV when you called.
He wasn't (was not) working when she arrived.
What were you doing when I called?
Future with Going to
He's (is) going to fly to Boston next week.
They're (are) not going to invite the Browns.
Where are you going to stay?
I play tennis on Mondays.
They don't (do not) work in New York.
Does she know him?
Simple Past
She went to Paris last week.
They didn't (did not) drive to work.
Where did she get that hat?
Simple Future
I'll (will) meet you at the airport tomorrow.
He won't (will not) be able to come.
Will they visit us soon?
Present Continuous
He's (is) working at the moment.
They aren't (are not) coming this evening.
What are you doing?
Past Continuous
I was watching TV when you called.
He wasn't (was not) working when she arrived.
What were you doing when I called?
Future with Going to
He's (is) going to fly to Boston next week.
They're (are) not going to invite the Browns.
Where are you going to stay?
The Past Simple Tense
مثلا: Last week, I played football.
[COLOR=window****]2- ملاحظة: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****]بعض الكلمات تدل على أن الجملة في الماضي البسيط: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****]yesterday -ago -last...[/COLOR][COLOR=window****][/COLOR]
3- يوضع الفعل في زمن الماضي البسيط في التصريف الثاني بإضافة ed إلى آخر الفعل إذا كان الفعل منتظما أو على حسب
I / You / He / She / It / We / You / They
played / studied / ran / drank
4- يتكون النفي في الماضي البسيط بإضافة كلمة didn't قبل الفعل و يوضع الفعل في التصريف الأول
play
didn't
played
study
didn't
studied
go
didn't
went
drive
didn't
drove
5- عند تكوين السؤال في الماضي البسيط نضع الفعل المساعد did قبل الفاعل و نضع الفعل في التصريف الأول بعد الفاعل.
I played football. جملة
Did you play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What did you play ? سؤال معلومات
Did you play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What did you play ? سؤال معلومات
6- عند الإجابة على سؤال معلومات يبدأ wh-word نقوم بحذف أداة الإستفهام و نحذف الفعل المساعد did ثم نبدأ بالفاعل و نضع الفعل في التصريف الثاني ثم نذكر الإجابة.
What did she study ? سؤال معلومات
She studied biology. إجابة
She studied biology. إجابة
The Present Simple Tense زمن المضارع البسيط
I play football on Wednesdays. The sun rises in the east. He teaches English.
[COLOR=window****]2- ملاحظة: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****]بعض الكلمات تدل على أن الجملة في المضارع البسيط: [/COLOR][COLOR=window****] every – always – sometimes – usually – on Fridays[/COLOR]3- يوضع الفعل في زمن المضارع البسيط في التصريف الأول و بإضافة s إلى آخر الفعل
play / study / run / drink
I / You / We / They
plays / studies / runs / goes
He / She / It /
play
doesn't
plays
study
doesn't
studies
go
don't
run
drive
don't
drive
5- عند تكوين السؤال في الماضي البسيط نضع كلمة do / does قبل الفاعل و نضع الفعل في التصريف الأول بعد الفاعل.He plays football. جملة
Does he play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What does he play ? سؤال معلومات
They play football. جملة
Do they play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What do they play ? سؤال معلومات
6- عند الإجابة على سؤال معلومات يبدأ wh-word نقوم بحذف أداة الاستفهام و نحذف الفعل المساعد do / does ثم نبدأ بالفاعل و نضع الفعل ثم نذكر الإجابة. Does he play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What does he play ? سؤال معلومات
They play football. جملة
Do they play football? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What do they play ? سؤال معلومات
What do they like ? سؤال معلومات
They like travelling. إجابة
What does he read ? سؤال معلومات
He reads newspapers. إجابة
*******************************************************************************************
They like travelling. إجابة
What does he read ? سؤال معلومات
He reads newspapers. إجابة
*******************************************************************************************
The Future المستقبل
1- نستخدم المستقبل عندما نريد أن نتحدث عن شيء ننوي القيام به أو شيء سوف يحصل في المستقبل.مثلا:
I will travel tomorrow. He is going to buy a car. They are coming next Saturday.
2- بعض الكلمات تستخدم مع زمن المستقبل مثل next – tomorrow - in the future
3- هناك ثلاث طرق للتحدث عن المستقبل:
أولا : باستخدام will و نضع الفعل في التصريف الأول
I / You / He / She / It / We / You / They + will + verb 1
My father will buy a car next year.
أ- عند النفي نضيف not إلى will I / You / He / She / It / We / You / They + will + not + verb 1
ب- تكوين السؤال نضع will قبل الفاعل
Will +I / You / He / She / It / We / You / They + verb 1 ?
He will see you next week. جملة
Will he see you next week ? سؤال بنعم أو لا
When will he see you? سؤال معلومات
الإجابة.
What will they watch ? سؤال معلومات
They will watch a match. إجابة
They will watch a match. إجابة
ثانيا: باستخدام going to :
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم going to ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول
verb 1
going to
am
I
is
He / She / It
are
We / You / They
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
verb 1
going to
not
am
I
not
is
He / She / It
not
are
We / You / They
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
verb 1…?
going to
I
Am
He / She / It
Is
We / You / They
Are
He is going to buy a ticket. جملة
Is he going to buy a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he going to buy? سؤال معلومات
Is he going to buy a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he going to buy? سؤال معلومات
ثانيا: باستخدام الفعل + am / is / are + الفعل + ing :
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول مضافا إليه -ing
verb 1+ -ing
am
I
is
He / She / It
are
We / You / They
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
verb 1+ -ing
not
am
I
not
is
He / She / It
not
are
We / You / They
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
verb + -ing?
I
Am
He / She / It
Is
We / You / They
Are
He is buying a ticket. جملة
Is he buying a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he buying ? سؤال معلومات
*******************************************************************************************Is he buying a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he buying ? سؤال معلومات
The Present Continuous المضارع المستمر
1- يستخدم المضارع المستمر لوصف حدث يقع في هذه اللحظة ( الآن ) 2- بعض الكلمات تستخدم مع المضارع المستمر مثل now – right now - at the moment
أ- نضع am / is / are بعد الفاعل ثم الفعل في التصريف الأول مضافا إليه -ing
verb 1+ -ing
am
I
is
He / She / It
are
We / You / They
ب – عند النفي نضيف not إلى am / is / are
verb 1+ -ing
not
am
I
not
is
He / She / It
not
are
We / You / They
ج- عند تكوين السؤال نقدم am / is / are على الفاعل
verb 1+ -ing?
I
Am
He / She / It
Is
We / You / They
Are
He is buying a ticket. جملة
Is he buying a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he buying ? سؤال معلومات
Is he buying a ticket? سؤال بنعم أو لا
What is he buying ? سؤال معلومات
Adjectives الصفات
1- تذكر الصفة بعد الفعل. و الصفات مثل
tall
short
bad
big
heavy
delicious
hungry
excellent
طويل
قصير
سيء
كبير
ثقيل
لذيذ
جائع
ممتاز
The restaurant is nice. The food is delicious.
It is a nice restaurant. He is a good player.
و لا نضع a إذا كان الموصوف جمعا أو غير معدود. مثل
They are tall men. It is delicious food.
*******************************************************************************************
*******************************************************************************************
Very and Too
تستخدم very مع الصفة فتجعل الصفة أقوى و تستخدم ( too ) مع الصفة فتفيد أن هذا الشيء أو الكمية أو الدرجة أكثر مما هو مطلوب أو مقبول ,
Ahmad runs 5 km every day. He is very healthy.
يجري احمد 5 كم يوميا. انه صحي جدا. I cannot drink this tea. It is too hot.
لا أستطيع أن أدخل في السيارة. السقف منخفض جدا ( استحالة الدخول في السيارة ) *******************************************************************************************
صفة
من التراكيب التي تستخدم في الكتابة المصدر + to …
It is easy to write stories. It is nice to meet you.
نبدأ الجملة بـ It is ثم نذكر الصفة و هي آخر كلمة في الجملة ثم نكمل الجملة من بدايتها. *******************************************************************************************
التوتوهات
م
شكل الكلمة
المعني
مثال
1
Two
رقم 2
She has two friends.
2
to
إلي
I go to school at seven.
3
to
إلًا
It is quarter to nine.
4
to
لكي - أن
Gamal studies English to be a doctor.
I want to say soething.
I want to say soething.
5
too
أيضاً
I like oranges and watermelons too.
6
too
جداً
Hayam is too fat . She mustn't eat much rice.
could you تعني أني أنا أطلب منك أنت. لاحظ الفرق بين الإجابتين.
Could العرض و الطلب باستخدام
Could العرض و الطلب باستخدام
could you move the chair ,please ? ………… yes, of course.
could you open the window, please? ………... No. sorry. It is cold today.
could I تعني أني أنا أعرض عليك أنت خدماتي . لاحظ الفرق بين الإجابتين.
could I move the chair for you ? ……. Yes . please.
could I carry the bag for you? No. thanks . I can do it by myself
could you open the window, please? ………... No. sorry. It is cold today.
could I تعني أني أنا أعرض عليك أنت خدماتي . لاحظ الفرق بين الإجابتين.
could I move the chair for you ? ……. Yes . please.
could I carry the bag for you? No. thanks . I can do it by myself
جدول الضمائر و صفات الملكية
ضمائر الفاعل
ضمائر المفعول
الضمائر المنعكسة
صفات الملكية
I أنا
me ي
myself
my ي
you أنت - أنتم
you ك – كم
Yourself
yourselves
Your ك – كم
he هو
him ه
himself
his ه
she هى
her ها
herself
her ها
it هي - هو
it ه - ها
itself
Its ه – ها
they هم
them هم
themselves
Their هم
we نحن
us نا
ourselves
our نا
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
The verb ''to have''
I have – أنا عندي
You Have – أنتَ عندك
You Have – أنتِ عندك
He/it has – هو عنده
She/it has – هي عندنا
We have – نحن عندنا
You have – أنتم عندكم
You have – أنتن عندكن
They have – هن عندهم
They have – هن عندهن
I had – كان عندي
You had – كان عندكَ
You had – كان عندكِ
He/it had – كان عنده
She/it had – كان عندها
We had – كان عندنا
You had – كان عندكم
You had – كان عندكن
They had – كان عندهن
They had – كان عندهن
I will have – سيكون عندي
You will have – سيكون عندك
You will have – سيكون عندكِ
He/it will have – سيكون عندها
She/it will have – سيكون عنده
We will have – سيكون عندنا
You will have – سيكون عندكم
They will have – سيكون عندهم
They will have – سيكون عندهن
I have – أنا عندي
You Have – أنتَ عندك
You Have – أنتِ عندك
He/it has – هو عنده
She/it has – هي عندنا
We have – نحن عندنا
You have – أنتم عندكم
You have – أنتن عندكن
They have – هن عندهم
They have – هن عندهن
I had – كان عندي
You had – كان عندكَ
You had – كان عندكِ
He/it had – كان عنده
She/it had – كان عندها
We had – كان عندنا
You had – كان عندكم
You had – كان عندكن
They had – كان عندهن
They had – كان عندهن
I will have – سيكون عندي
You will have – سيكون عندك
You will have – سيكون عندكِ
He/it will have – سيكون عندها
She/it will have – سيكون عنده
We will have – سيكون عندنا
You will have – سيكون عندكم
They will have – سيكون عندهم
They will have – سيكون عندهن
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
The verb
To be mistaken - أخطأ
To drive - ساق
To validate - ثبت
To fortify - قوى
To danse - رقص
To sing - غنى
To weep - بكى
To vote - صوت
To try - حاول
To steal - سرق
To work - اشتغل
To swim - سبح
To go away - ابتعد
To make way - إتجه
To answer - أجاب
To meet - اجتمع
To love - أحب
To respect - احترم
To preserve - احتفظ
To choose - اختار
To take - أخذ
To print - طبع
To hide - أخفى
To satisfy - أرضى
To get rady - استعد
To want - أراد
To uso – استعمل
He speaks - يتكلم
He walks - يمشي
He Sings - يغني
He dances - يرقص
He works - يعمل
He tries - يحاول
He swims - يسبح
He weeps - يبكي
He anounces - يعلن
He publishes - ينشر
He boasts - يفخم
He speaks/spoke - يتكلم/تكلم
He walks/walked - يمشي/مشى
He sings/sang - يغني/غنى
He dances/danced - يرقص/رقص
He works/worked - يعمل/عمل
He tries/tried - يحاول/حاول
He swims/swam – يسبح/سبح
He weeps/wept - يبكي/بكى
He publishes/publilshed - ينشر/نشر
He boasts/boasted - يفخم/فخم
To be mistaken - أخطأ
To drive - ساق
To validate - ثبت
To fortify - قوى
To danse - رقص
To sing - غنى
To weep - بكى
To vote - صوت
To try - حاول
To steal - سرق
To work - اشتغل
To swim - سبح
To go away - ابتعد
To make way - إتجه
To answer - أجاب
To meet - اجتمع
To love - أحب
To respect - احترم
To preserve - احتفظ
To choose - اختار
To take - أخذ
To print - طبع
To hide - أخفى
To satisfy - أرضى
To get rady - استعد
To want - أراد
To uso – استعمل
He speaks - يتكلم
He walks - يمشي
He Sings - يغني
He dances - يرقص
He works - يعمل
He tries - يحاول
He swims - يسبح
He weeps - يبكي
He anounces - يعلن
He publishes - ينشر
He boasts - يفخم
He speaks/spoke - يتكلم/تكلم
He walks/walked - يمشي/مشى
He sings/sang - يغني/غنى
He dances/danced - يرقص/رقص
He works/worked - يعمل/عمل
He tries/tried - يحاول/حاول
He swims/swam – يسبح/سبح
He weeps/wept - يبكي/بكى
He publishes/publilshed - ينشر/نشر
He boasts/boasted - يفخم/فخم
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
ظرف النوع
Adverb of manner
Good - جيد
Enough good - مستحسن
Better - أحسن
The best - أفضل
Bad - سيئ
Worse - أسوأ
The worst - أرذأ
Rapidly - سريعا
Yes - نعم
No - لا
Rather - بالأحرى
Sure - أكيد
Willingly - طوعا
Wisely - بحكمة
Slowly - مهلا
Adverb of manner
Good - جيد
Enough good - مستحسن
Better - أحسن
The best - أفضل
Bad - سيئ
Worse - أسوأ
The worst - أرذأ
Rapidly - سريعا
Yes - نعم
No - لا
Rather - بالأحرى
Sure - أكيد
Willingly - طوعا
Wisely - بحكمة
Slowly - مهلا
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
learn Adverb of time in English

ظرف الزمان
Adverb of time
Today - اليوم
Tomorrow - غدا
After tomorrow – بعد غد
Yestarday - الأمس
The day before – قبل أمس
Eve - عشية
Next year – السنة المقبلة
last year – السنة الماضية
Sunrise - شروق
Sunset - غروب
Present - حاضر
Past - ماضي
Now - الأن
Soon – بعد قليل
After - بعد
Formerly - قديما
Then - عندئد
Always - دائما
Never - أبدا
Sooner - قريبا
Henceforth – بعد الأن
Again - أيضا
Already – من قبل
Early - مبكرا
Lately - متأخرا
In the future – في المستقبل
From now on – من الآن فصاعدا
Then, After – ثم، من بعد
Before - أنفا
At once - فورا

ظرف الزمان
Adverb of time
Today - اليوم
Tomorrow - غدا
After tomorrow – بعد غد
Yestarday - الأمس
The day before – قبل أمس
Eve - عشية
Next year – السنة المقبلة
last year – السنة الماضية
Sunrise - شروق
Sunset - غروب
Present - حاضر
Past - ماضي
Now - الأن
Soon – بعد قليل
After - بعد
Formerly - قديما
Then - عندئد
Always - دائما
Never - أبدا
Sooner - قريبا
Henceforth – بعد الأن
Again - أيضا
Already – من قبل
Early - مبكرا
Lately - متأخرا
In the future – في المستقبل
From now on – من الآن فصاعدا
Then, After – ثم، من بعد
Before - أنفا
At once - فورا
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
ظرف المكان
Adverb of place
Elsewhere – إلى غير محل
Here - هنا
There - هناك
Inside - داخل
Outside - خارج
In front of - أمام
Behind - خلف
Far - بعيد
Below - أسفل
Above - أعلى
Beyond – من هناك
Every where – في كل مكان
Where - حيث
Under - تحت
On, Above - فوق
Adverb of place
Elsewhere – إلى غير محل
Here - هنا
There - هناك
Inside - داخل
Outside - خارج
In front of - أمام
Behind - خلف
Far - بعيد
Below - أسفل
Above - أعلى
Beyond – من هناك
Every where – في كل مكان
Where - حيث
Under - تحت
On, Above - فوق
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
تعلم الكميات باللغة الانجليزية
learn Quantity in English
Quantity
Enough – كفاية/بما فيه الكفاية
Much - كثيرا
Very – جدا/لغاية ما يكون
Little - قليل
More - أكثر/زيادة
Less - أقل
How many – (كم (العدد
How much – (كم (الكمية
So much – حتى أن
Too – بهذا المقدار
The least - أدنى
Excess - زيادة
Shortage - نقص
Every thing – كل شيء
No thing – لا شيء
learn Quantity in English
Quantity
Enough – كفاية/بما فيه الكفاية
Much - كثيرا
Very – جدا/لغاية ما يكون
Little - قليل
More - أكثر/زيادة
Less - أقل
How many – (كم (العدد
How much – (كم (الكمية
So much – حتى أن
Too – بهذا المقدار
The least - أدنى
Excess - زيادة
Shortage - نقص
Every thing – كل شيء
No thing – لا شيء
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
تعلم حروف الجر والعطف باللغة الانجليزية
learn Prepositions and conjunctions in English

حروف الجر والعطف
Prepositions and conjunctions
In - في
From - من
To - إلى
At - عند
To, Towards - نحو
With - مع
Then - ثم
Finally - أخيرا
On - على
For - لأجل
Because of - بسبب
Like - مثل
Almost - تقريبا
Enough - كفى
Litle, Few - قليلا
learn Prepositions and conjunctions in English

حروف الجر والعطف
Prepositions and conjunctions
In - في
From - من
To - إلى
At - عند
To, Towards - نحو
With - مع
Then - ثم
Finally - أخيرا
On - على
For - لأجل
Because of - بسبب
Like - مثل
Almost - تقريبا
Enough - كفى
Litle, Few - قليلا
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
تعلم صفات الملكية باللغة الانجليزية
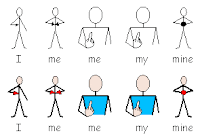
learn Possessive adjectives in English
learn Possessive adjectives in English
الصابرة المحتسبة
**مشرفة قسم ذوي الإعاقة **
تعلم أسماء الإشارة باللغة الانجليزية
learn Demonstratives in English

أسماء الإشارة
Demonstratives
This - هذا-هذه
These - هؤلاء
That - ذلك-تلك
Those - أولئك
This soldier – هذا الجندي
This book – هذا الكتاب
That man – ذلك الرجل
That summer – ذلك الصيف
This watch – هذه الساعة
That idea – تلك الفكرة
These passengers – هؤلاء المسافرين
Those Singers – أولئك المغنيون
learn Demonstratives in English

أسماء الإشارة
Demonstratives
This - هذا-هذه
These - هؤلاء
That - ذلك-تلك
Those - أولئك
This soldier – هذا الجندي
This book – هذا الكتاب
That man – ذلك الرجل
That summer – ذلك الصيف
This watch – هذه الساعة
That idea – تلك الفكرة
These passengers – هؤلاء المسافرين
Those Singers – أولئك المغنيون